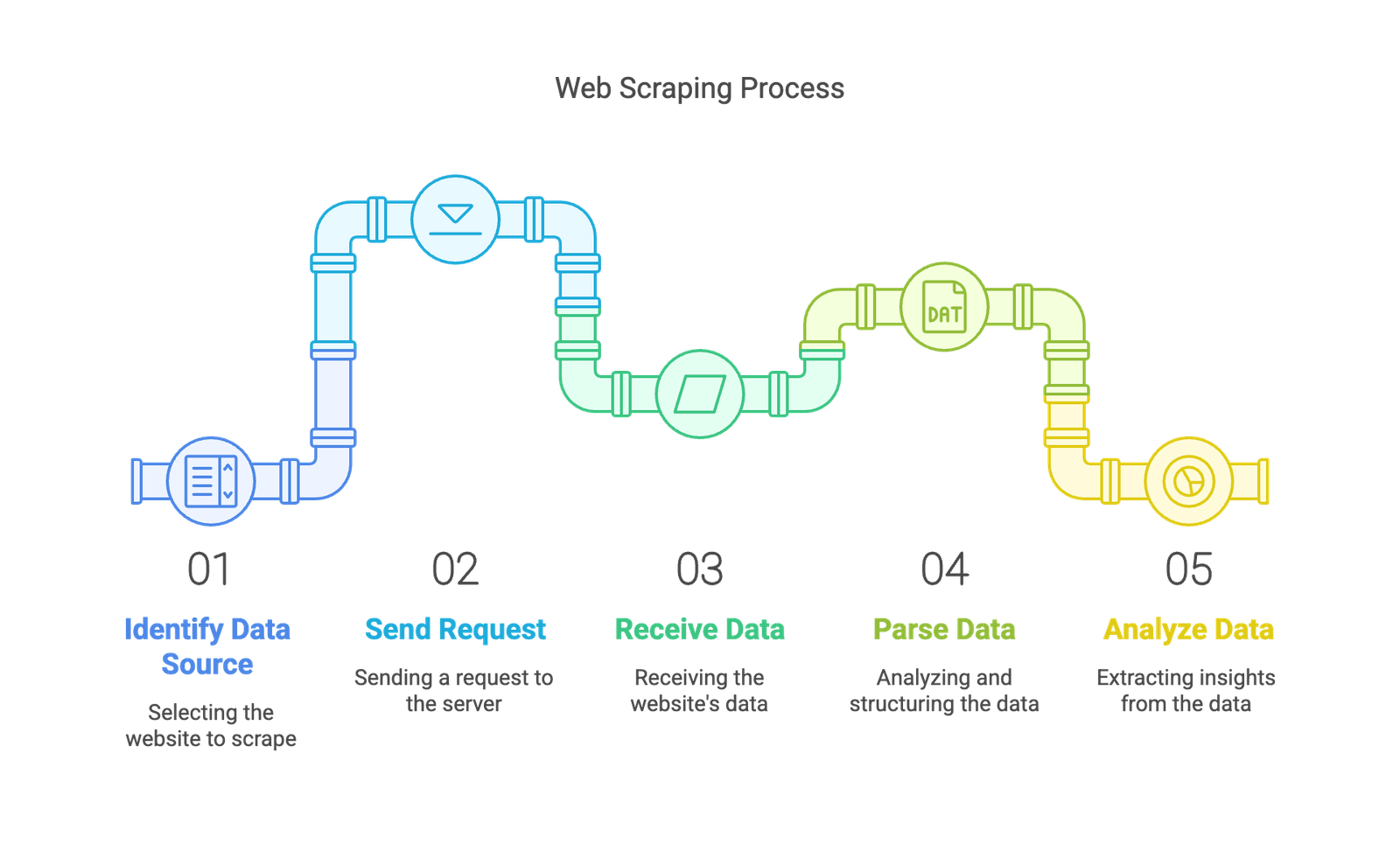
1️⃣ What is Web Scraping?
👉 Web Scraping is the process of extracting data from websites automatically using code. It allows us to collect, parse, and analyze web data without manual copying.
📌 Common Uses of Web Scraping:
✔ Extracting product prices from e-commerce websites.
✔ Collecting news articles or blog posts.
✔ Gathering stock market or weather data.
✔ Analyzing social media data.
📌 Popular Python Libraries for Web Scraping:
- requests → Fetches HTML content from web pages.
- BeautifulSoup → Parses and extracts data from HTML/XML.
- selenium → Handles dynamic JavaScript-based websites.
2️⃣ requests Library (Fetching Web Pages)
✅ Installing requests
pip install requests |
✅ Fetching a Web Page
import requests url = "https://www.example.com" response = requests.get(url) # Sending an HTTP GET requestprint("Status Code:", response.status_code) # 200 = Success print("Page Content:", response.text[:500]) # Print first 500 characters |
📌 Output:
| Status Code: 200 Page Content: <html><head><title>Example Domain</title></head>... |
✅ Checking Response Details
| print("Status Code:", response.status_code) # HTTP response code print("Headers:", response.headers) # Response headers print("Encoding:", response.encoding) # Character encoding print("Cookies:", response.cookies) # Cookies from the response |
3️⃣ BeautifulSoup Library (Parsing HTML)
✅ Installing BeautifulSoup
| pip install beautifulsoup4 |
✅ Parsing an HTML Page
| from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import requests url = "https://www.example.com" response = requests.get(url) soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser") # Parse HTML print("Page Title:", soup.title.text) # Extract the title print("First Paragraph:", soup.p.text) # Extract first paragraph |
📌 Output:
| Page Title: Example Domain First Paragraph: This domain is for use in illustrative examples... |
4️⃣ Extracting Specific Elements
✅ Finding All Links (<a> Tags)
| for link in soup.find_all("a"): print("Link:", link.get("href")) |
✅ Extracting Text from a Specific Tag
| heading = soup.find("h1") # Finds the first <h1> tag print("Heading:", heading.text) |
5️⃣ Example: Scraping Quotes from a Website
We will scrape quotes from http://quotes.toscrape.com.
| import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup url = "http://quotes.toscrape.com" response = requests.get(url) soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, "html.parser") # Extract all quotes quotes = soup.find_all("span", class_="text") for quote in quotes: print(quote.text) # Print each quote |
📌 Output:
| “The greatest glory in living lies not in never falling, but in rising every time we fall.” “The way to get started is to quit talking and begin doing.” ... |
6️⃣ Handling Headers & User Agents
Some websites block automated scraping. Use headers to mimic a real user:
| headers = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0"} response = requests.get(url, headers=headers) |
🔹 Summary
✔ requests → Fetches HTML content from websites.
✔ BeautifulSoup → Parses and extracts data from HTML.
✔ Use soup.find() and soup.find_all() to extract specific elements.
✔ Add headers to avoid detection by websites.